This tutorial is designed for beginners who want to get started with PROC SQL. It also includes a detailed comparison of the functions used in SAS and PROC SQL.
The syntax of PROC SQL is as follows:
PROC SQL; SELECT column(s) FROM table(s) | view(s) WHERE expression GROUP BY column(s) HAVING expression ORDER BY column(s); QUIT;
The SQL statements must be specified in the following order:
Note : SELECT FROM clauses are required. All the other clauses are optional.
PROC SQL statement calls the SQL procedure and QUIT statement ends the procedure.
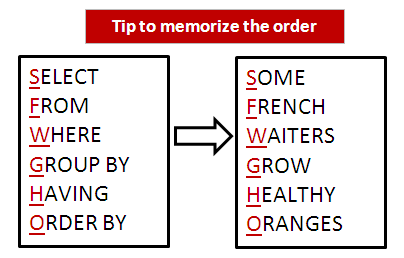
To memorize the order of SQL queries, you can use the mnemonic "SFWGHO".

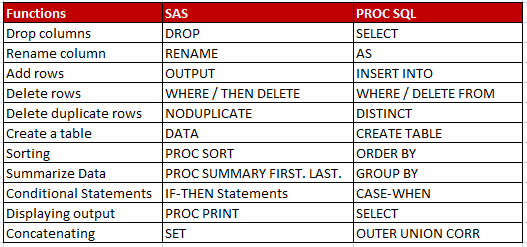
We are going to look at the difference between SAS and PROC SQL.
| SAS | SQL |
|---|---|
| Dataset | Table |
| Observation | Row |
| Variable | Column |
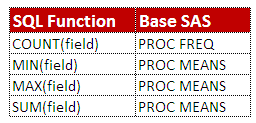
| Functions | SAS | PROC SQL |
|---|---|---|
| Select/Drop columns | KEEP / DROP | SELECT |
| Rename column | RENAME | AS |
| Add rows | OUTPUT | INSERT INTO |
| Delete rows | WHERE/THEN DELETE | WHERE / DELETE FROM |
| Delete duplicate rows | NODUPLICATE | DISTINCT |
| Create a table | DATA | CREATE TABLE |
| Sorting | PROC SORT | ORDER BY |
| Summarize Data | PROC SUMMARY, FIRST. LAST. | GROUP BY |
| Conditional Statements | IF-THEN Statements | CASE-WHEN |
| Displaying output | PROC PRINT | SELECT |
| Concatenating | SET | OUTER UNION CORR |
You would hear the word 'schema' from SQL programmers. It refers to design of database. In other words, it is the framework of database.
Sample DatasetIn the SAS program below, we are creating sample data for illustration purposes by extracting a few observations from the dataset "BWEIGHT" stored in the SASHELP library.
data outdata ; set SASHELP.BWEIGHT (obs=1000); run;
proc sql; select * from outdata; Quit;
Asterisk (*) is used to select all columns (variables) in the order in which they are stored in the table. Outdata is the table (dataset) from which we need to select the columns.
To display the list of columns to the SAS log, use FEEDBACK option in the PROC SQL statement.
proc sql feedback; select * from outdata; Quit;
The SAS log is shown below:
71 proc sql feedback; 72 select * 73 from outdata; NOTE: Statement transforms to: select OUTDATA.Weight, OUTDATA.Black, OUTDATA.Married, OUTDATA.Boy, OUTDATA.MomAge, OUTDATA.MomSmoke, OUTDATA.CigsPerDay, OUTDATA.MomWtGain, OUTDATA.Visit, OUTDATA.MomEdLevel from outdata; 74 Quit;2. How to Select Specific Variables from Dataset
In the SELECT clause, multiple columns are separated by commas.
proc sql; select weight,married from outdata; Quit;
In the SELECT clause, Weight and Married columns are specified so that we can select them from OUTDATA table.
3. How to limit the number of rowsSuppose you want to limit the number of rows that PROC SQL displays, use the OUTOBS= option in the PROC SQL statement.
proc sql outobs=50; select weight,married from outdata; Quit;4. How to Rename a Variable
Suppose you want to rename a variable, use the column alias AS option in the PROC SQL statement.
options nolabel; proc sql; select weight,married as marriage from outdata; Quit;
The variable name has been renamed from married to marriage. options nolabel tells SAS not to use variable labels in SAS procedures. I used it so that you can see variable name has been changed to marriage.
5. How to Create a New VariableSuppose you want to create a new variable that contains calculation.
proc sql; select weight, (weight*0.5) as newweight from outdata; Quit;
A new variable has been created and named newweight which is calculated on the basis of the existing variable weight.
6. How to refer to a previously calculated variableThe keyword CALCULATED is used to refer a previously calculated variable.
proc sql; select weight, (weight*0.5) as newweight, CALCULATED newweight*0.25 as revweight from outdata; Quit;7. How to Remove Duplicate Rows
The keyword DISTINCT is used to eliminate duplicate rows from your query results.
In the following program, we are asking SAS to remove all those cases where in duplicates exist on combination of both the variables - weight and married.
proc sql; select DISTINCT weight, married from outdata; quit;
The DISTINCT * implies cases having same values in all the variables as a whole would be removed.
proc sql; select DISTINCT * from outdata; quit;8. How to Label and Format Variables
SAS-defined formats can be used to improve the appearance of the body of a report. You can also label the variables using LABEL keyword.
options label; proc sql; select weight FORMAT= 8.2 , married Label =" Married People" from outdata; Quit;9. How to Sort Data
The ORDER BY clause returns the data in sorted order.
ASC option is used to sort the data in ascending order. It is the default option. DESC option is used to sort the data in descending order.
proc sql; select MoMAge, eight, married from outdata ORDER BY weight ASC, married DESC; Quit;10. How to Filter Data with WHERE clause
Use the WHERE clause with any valid SAS expression to subset data.
List of conditional operators : 1. BETWEEN-ANDThe BETWEEN-AND operator selects within an inclusive range of values.
Example : where salary between 4500 and 6000;
2. CONTAINS or ?The CONTAINS or ? operator selects observations by searching for a specified set of characters within the values of a character variable.
Example : where firstname contains 'DE';
OR
where firstname ? 'DE';
The IN operator selects from a list of fixed values.
Example : where state = 'NC' or state = 'TX';
The easier way to write the above statement would be to use the IN operator.
where state IN ('NC','TX');
4. IS MISSING or IS NULLThe IS MISSING or IS NULL operator selects missing values.
Example : where dateofbirth is missing
OR where dateofbirth is null
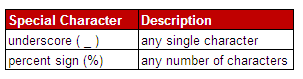
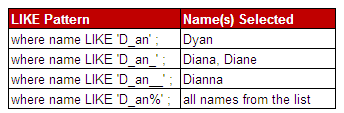
The LIKE Operator is used to select a pattern.
Important Point :
The WHERE clause can reference a previously calculated variable in two ways-
1. Use CALCULATED keyword.
2. Repeat the calculation in the WHERE clause.
PROC SQL; SELECT momage, (WEIGHT * .01) AS NEWWEIGHT FROM outdata WHERE CALCULATED NEWWEIGHT > 5; QUIT;Method II :
PROC SQL; SELECT momage, (WEIGHT * .01) AS NEWWEIGHT FROM outdata WHERE (WEIGHT * .01) > 5; QUIT;11. How to Write Multiple Conditions/Criteria in PROC SQL
The CASE WHEN statement is used in SQL to perform conditional logic and return different values based on specified conditions. The END statement is required when using the CASE WHEN statement.
PROC SQL; SELECT WEIGHT, CASE WHEN WEIGHT BETWEEN 0 AND 2000 THEN 'LOW' WHEN WEIGHT BETWEEN 2001 AND 3000 THEN 'MEDIUM' WHEN WEIGHT BETWEEN 3001 AND 4000 THEN 'HIGH' ELSE 'VERY HIGH' END AS NEWWEIGHT FROM outdata; QUIT;
The conditions within the CASE statement are as follows:
The following operators can be used in CASE expression:
Use GROUP BY clause to summarize or aggregate data. Summary functions are used on the SELECT statement to produce summary for each of the analysis variables.
proc sql; select momage, COUNT(married) AS marriage from outdata GROUP BY momage; Quit;
In order to subset data when grouping is in effect, the HAVING clause must be used.The variable specified in having clause must contain summary statistics.
proc sql; select momage, weight, COUNT(married) AS marriage from outdata GROUP BY momage, weight HAVING marriage > 2; Quit;
Important Point -
The WHERE clause cannot be used to subset aggregated data. To subset data with the GROUP BY clause you must use HAVING clause.
14. How to Create a New TableThe CREATE TABLE statement can be used to create a new data set as output instead of a report produced in output window.
PROC SQL; CREATE TABLE table-name AS SELECT column(s) FROM table(s) | view(s) WHERE expression GROUP BY column(s) ORDER BY column(s); QUIT;
proc sql; create table health AS select weight, married from outdata ORDER BY weight ASC, married DESC; Quit;15. How to limit the number of rows in newly created dataset?
Suppose you want to limit the number of rows that PROC SQL produces in the data set, use the INOBS= option in the PROC SQL statement.
proc sql INOBS=50; create table health AS select weight,married from outdata; Quit;Difference between INOBS= and OUTOBS=
INOBS controls how many records are read from the dataset and OUTOBS controls how many records are written. Run the following program and see the difference. Both returns different results.
/* OUTOBS=Example*/ proc sql outobs=2; select age, count(*) as tot from sashelp.class group by age; quit; /* INOBS= Example */ proc sql inobs=4; select age, count(*) as tot from sashelp.class group by age; quit;16. How to count unique values by a grouping variable
Suppose you are asked to calculate the unique number of age values by Sex columns using SASHELP.CLASS dataset.
You can use PROC SQL with COUNT(DISTINCT variable_name) to determine the number of unique values for a column.
PROC SQL; CREATE TABLE TEST1 as SELECT Sex, Count(distinct Age) AS Unique_count FROM sashelp.class GROUP BY Sex; QUIT;17. How to count the number of missing values
You can use NMISS() function to compute the number of missing values in a variable. The COUNT() function returns the number of non-missing values in a variable.
data temp; input id; cards; 1 2 . 4 5 . ; run;
proc sql; select nmiss(id) as N_missings, count(id) as N, calculated N_missings + calculated N as total from temp; quit;
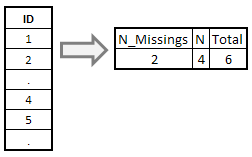
How to refer to a calculated variable
The keyword CALCULATED is used to refer to a newly created variable for further calculation. In this case, we have used CALCULATED to sum 'N_MISSINGS' and 'N' variables.
18. KEEP and DROP some variablesSuppose you need to keep all the variables from SASHELP.CARS except variables 'MODEL' and 'MAKE'. The DROP= option is used to drop these two variables. Similarly, we can use KEEP= option to keep specific variables. These DROP= and KEEP= Options are not native SQL language. It only works in SAS.
proc sql; create table saslearning (drop= make model) as select * from sashelp.cars; quit;19. How to delete rows from a table
You can use DELETE FROM statement to remove records (rows) from a dataset.
proc sql; delete from outdata where momage > 0; quit;
In this case, we are deleting all records having momage greater than 0 from outdata dataset. Log shows '478 rows were deleted from outdata'.
20. How to use sub query in PROC SQL?Suppose you need to find out employee IDs having records in the table named 'file1' but not in table 'file2'. In the code below, we are querying multiple tables (datasets).
data file1; input ID age; cards; 1 24 2 34 3 45 4 67 ; run; data file2; input ID age; cards; 1 25 3 46 4 62 ; run; Proc SQL; Select ID from file1 Where ID not in (select ID from file2); Quit;21. Sub Query - Example II
Find employee IDs whose age is in the average age +/- 10 years.
Proc SQL; Select id from file1 where age between (select Avg(age) from file1) - 10 and (select avg(age) from file1)+10; Quit;22. Sub Query - Example III
In this example, the CASE statement is used to evaluate a condition: whether a student has a score below 70 in any test. To solve this, we have written a subquery that selects "Student_ID" from the "Tests" table where the "Score" is less than 70.
proc sql; select Name,Grade,Teacher, Case When Student_ID in (select Student_ID from Tests where Score lt 70) then 'Failed one or more tests' else 'Passed all tests' end as Test_Results from Students; quit;
If the condition is true, the new column "Test_Results" is assigned the value 'Failed one or more tests.' If the condition is false, the value 'Passed all tests' is assigned to the "Test_Results" column. The result of the query will return the student's name, grade, teacher, and their test results.
Next Lesson : PROC SQL Joins Related Posts SAS Tutorials : Top 100 SAS Tutorials Proc SQL Tutorials : Top 15 Proc SQL Tutorials Spread the Word!
About Author:
Deepanshu founded ListenData with a simple objective - Make analytics easy to understand and follow. He has over 10 years of experience in data science. During his tenure, he worked with global clients in various domains like Banking, Insurance, Private Equity, Telecom and HR.
While I love having friends who agree, I only learn from those who don't
Let's Get Connected Email LinkedIn
Well Done Deepanshu, I was almost new to SQL.
But Now I can say that atleast I have learnt basic steps and statements for PROC SQL.
Could you be so kind to share codes for joints as well. Reply Delete